
Nearly 62% of Bitcoin remains dormant, having not moved in over a year and earning no yield, despite its immense value and security. Traditional staking solutions often require users to relinquish custody, bridge, or wrap their Bitcoin, exposing them to significant risks and complexity. Core revolutionizes Bitcoin utility by enabling native, non-custodial staking directly from users’ wallets, without the need for wrapping, bridging, or compromising private keys.
To date, over 5,250 BTC have already been staked using Core's Self-Custodial Bitcoin staking mechanism. At the current price of Bitcoin, activating just 1% of dormant Bitcoin could unlock more than $15.3 billion in productive economic activity, without compromising the foundational principles of Bitcoin.
Core’s Breakthrough: Self-Custodial BTC Staking
In April 2024, the Core Foundation introduced the first-ever Self-Custodial Bitcoin staking solution, unlocking native Bitcoin yield while preserving complete user control. Here's how it works:
- Mechanism: Core leverages Bitcoin’s native CheckLockTimeVerify (CLTV) function, allowing users to time-lock their Bitcoin on the Bitcoin network for a chosen period.
- Yield: During the lock period, users earn CORE token rewards for securing the Core blockchain, all while their Bitcoin remains on the Bitcoin network, untouched by third parties.
- Custody: The timelocked Bitcoin remains under the complete custody of the users. Once the lock period ends, the Bitcoin is released back to the user, and all staking rewards in the form of CORE tokens are credited to them.
Your Bitcoin never leaves your wallet or the Bitcoin network: no custodians, no bridges - just secure, self-custodial staking and sustainable yield.
How Core's Self-Custodial Bitcoin Staking Works - Technical Workflow
Core's Self-Custodial Bitcoin Staking is on-chain coordination between the Bitcoin network and the Core blockchain, bridged by stateless relayers. Relayers serve as a vital link between the Bitcoin and the Core network, actively monitoring the Bitcoin network for valid Bitcoin staking transactions associated with Core validators.
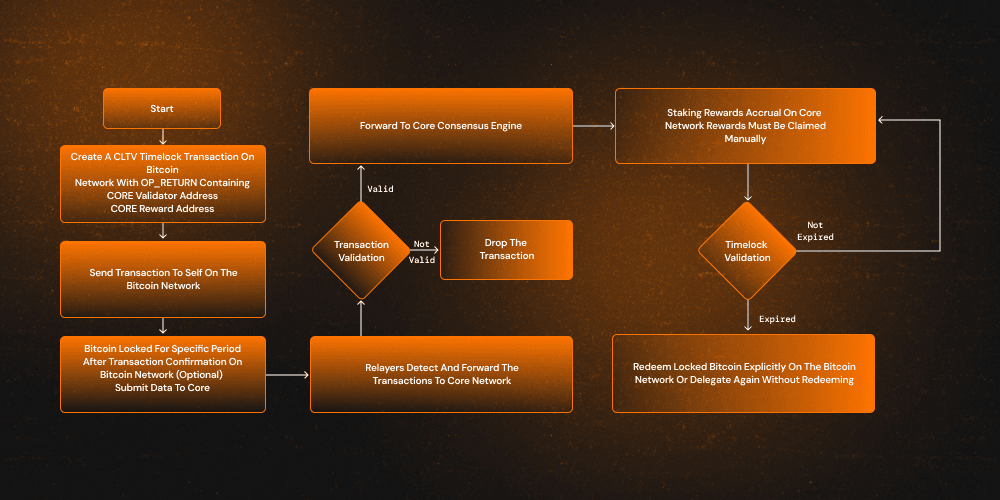
bitcoin staking technical workflow
The following is the workflow of how Core’s Self-Custodial Bitcoin Staking works:
- Stake Construction on Bitcoin:
Users initiate a timelock transaction with CLTV on the Bitcoin blockchain. This transaction includes:
Core Validator Address: The Identifier for the validator users wish to delegate their stake to.
CORE Reward Address: The user’s wallet address to receive the CORE token reward.
Self-Custody BTC Locking: Locking a certain amount of BTC by sending it to the user’s own Bitcoin address on the Bitcoin network, ensuring custodial control is retained.
- BTC Locking Mechanics: Once confirmed on the Bitcoin network, the CLTV-enforced transaction timelocks the BTC for the user-defined period.
- Relayer Detection & Cross-Chain Transmission:
Stateless relayers continuously scan the Bitcoin network for CLTV transactions containing valid OP_RETURN staking data. Upon detecting Bitcoin staking transactions, the relayers:
Validate the transaction's details and legitimacy.
Transmit the metadata to Core's consensus engine for processing and reward attribution.
For the transaction to be picked by the relayers:
The transaction must be sent to the user's own Bitcoin address.
Specifying the lock-up stake amount intended to be delegated.
The transaction must contain an OP_RETURN field.
- Validation on Core:
The Core network performs multiple validation checks on transactions.
If the transaction isn't valid, it is discarded.
If validated, the transaction is registered, staking records are updated, and the user becomes eligible for staking rewards.
- Staking Rewards Accrual:
Once a staking transaction is successfully registered on the Core network:
CORE token rewards begin accruing based on the amount of BTC locked and the selected validator.
Users are responsible for manually claiming their accrued rewards through the Core staking interface or supported wallets. Accrued CORE token rewards can be claimed daily. Further, to be eligible to earn rewards, it is required to complete a full staking round (00:00:00 - 23:59:29 UTC).
The Core consensus engine incorporates BTC staking weight into its hybrid score calculations, which determine the selection of validators for the active validator set.
- Timelock Expiry Validation:
On the Core network, checks are performed periodically to determine whether the Bitcoin timelock period has expired:
If the timelock period hasn't expired, the BTC remains locked, and rewards continue to accrue.
Once the timelock expires, the BTC becomes eligible for withdrawal or can be re-delegated for a new staking cycle
- Redeeming or Re-Staking BTC:
As the staking period ends, users have two options:
Redeem the locked BTC back on the Bitcoin network and claim staking rewards.
Re-delegate BTC for another staking round without redeeming it.
Throughout the process, the BTC never leaves the user’s wallet, ensuring full self-custody while generating high yields on the idle Bitcoin.
Script Construction: RedeemScript Breakdown
To stake Bitcoin non-custodially on Core using a staking script, users create a special Bitcoin script that locks their funds using a timelock. Core supports multiple Bitcoin script templates depending on the desired security model.
Using a Public Key:
undefined
<CLTV timelock> OP_CLTV OP_DROP<pubKey> OP_CHECKSIG
Unlocking Script:
<sig><RedeemScript>
Using a Public Key Hash (Recommended):
undefined
<CLTV timelock> OP_CLTV OP_DROP OP_DUP OP_HASH160<pubKey Hash> OP_EQUALVERIFY OP_CHECKSIG
Unlocking Script:
<sig><pubKey><RedeemScript>
Using Multi-Signature Address
undefined
<CLTV timelock> OP_CLTV OP_DROP M <pubKey1><pubKey2> ...<pubKeyN> N OP_CHECKMULTISIG
Unlocking Script:
OP_0<sig1> ...<sigM><RedeemScript>
The locked amount and duration specified in the staking script are crucial parameters that contribute to validator election and reward allocation.
OP_RETURN Metadata Encoding
Each staking transaction must include metadata that Core's relayers can recognize to validate transactions and proceed further. The OP_RETURN field stores metadata for the staking intent. It's how relayers recognize and forward the staking transaction to the Core network. The OP_RETURN output should contain all staking information in order and be composed in the following format:
OP_RETURN: Identifier (
0x6a)LENGTH: Total byte length after
OP_RETURNSAT+ Identifier: "SAT+" (4 bytes)
Version: 0x01 (1 byte)
Chain ID: 1114 for Core Testnet2 or 1116 for Core Mainnet (2 bytes)
Delegator: CORE reward address (20 bytes)
Validator: Core validator address to delegate BTC to (20 bytes)
Fee: Relayer fee in CORE (1 byte)
RedeemScript: Used for unlocking BTC post-timelock
(Optional) Timelock: 4 bytes (Little Endian if included)
Note that the total size of the OP_RETURN field is limited to 80 bytes on the Bitcoin mainnet. All staking metadata must fit within this constraint.
Data Encoding: Push Rules for Bitcoin Scripts
Bitcoin script follows specific rules for how data is pushed onto the stack. To ensure your OP_RETURN and RedeemScript work correctly, follow the rules for byte lengths and numeric values.
Numbers (0–16): Use
OP_0toOP_16Data < 76 bytes: Use length byte + Data
Data ≥ 76 and ≤ 255 bytes: Use
0x4c (OP_PUSHDATA1)+ Length + DataData > 255 and ≤ 65535 bytes: Use
0x4d (OP_PUSHDATA2)+ Length + DataData > 65535 bytes: Use
0x4e (OP_PUSHDATA4)+ Length + Data
Either RedeemScript or Timelock must be provided for the relayers to validate the transaction. If a RedeemScript is included, relayers use it as is. If it's not provided, relayers will generate it using the timelock and details from the transaction inputs.
Self-Custodial BTC Staking: Key Considerations
Minimum BTC Amount & Network Fees:
Staking through Core Staking Website: Minimum 0.01 BTC (plus network fees)
Staking through CLI Staking Script: No minimum
For short-term staking (under 1 month), consider a minimum of 0.05 BTC to offset potential fee spikes.
Staking Duration Requirements: The staking website UI enforces a 5-day minimum lockup, whereas staking through the CLI script has no minimum lockup requirements.
Bitcoin Staking Address Derivation: The staking address generated is different from your usual Bitcoin address, but your BTC remains fully in your control throughout the process.
Delay in Wallet Display of Locked BTC: After staking, there may be a delay (up to several hours) before your BTC appears as staked in your wallet due to network confirmations and congestion. You can check your staking status via Core’s staking website or a block explorer like Mempool.space.
Locking Strategy: During the lock period, your BTC is non-spendable, so choose your staking duration based on your liquidity needs and yield goals.
Timeline: It typically takes about 6 Bitcoin block confirmations (roughly 60 minutes) for your transaction to be processed, after which rewards start accruing within 24 hours.
For Developers: Integrating Self-Custodial BTC Staking
Core’s Self-Custodial Bitcoin Staking isn’t just about earning yield on idle BTC; it’s a flexible platform for developers to build Bitcoin-native financial apps that keep users in control of their assets.
By tapping into this Bitcoin-native staking layer on Core, developers can:
Build yield protocols, restaking layers, and automated staking tools.
Power Bitcoin-backed stablecoins and lending using locked BTC as collateral.
Leverage Bitcoin’s security and Core’s composability—no custody trade-offs.
Unlock several new use cases for transforming Bitcoin into a capital-efficient asset.
Conclusion
Core’s Self-Custodial Bitcoin Staking offers the first truly self-custodial, Bitcoin-native staking solution. Your Bitcoin stays in your wallet—no custodians, no bridges, just secure staking. Core enables you to earn a yield on your Bitcoin securely, natively, and without compromising control.
Ready to put your Bitcoin to work safely?
Stake: Visit Core’s staking portal and start earning yield on your idle BTC.